I want to tell you about a man named Mark. He’s 58, lives in a remote town surrounded by the kind of rugged green beauty that draws tourists in but is a medical desert. For Mark, the nearest cardiac care unit is three hours out; getting a basic heart scan isn’t just inconvenient—it could be a matter of life and death. Having already lost a couple of family members to heart disease, every twinge in his chest sets off a chain reaction of anxiety: What if this is the moment he’s been dreading?
I’ve thought about Mark a lot in my work at GE HealthCare, because his fear is real, and his situation isn’t rare. According to the CDC, around 700,000 Americans die each year from heart disease1 , and the World Health Organization estimates that number balloons to nearly 18 million across the world.[2] What’s especially heart-wrenching is that nearly half of all heart failure patients had symptoms for months before they were finally diagnosed.
We don’t yet have a holistic cure for the illness, but we do know that adverse events arising from cardiac disease can be prevented if it is caught early. Finally, we have a way to do just that for people like Mark. With ultrasound paired with artificial intelligence (AI),we can enable non-expert medical practitioners in medical deserts to capture high-quality images , reimagining access to care itself.
The GE HealthCare solution combines three capabilities that work together as one system: AI-powered real-time probe guidance features show you where to move the probe, and automated quality meters display how sharp the picture is. In addition, cloud connectors stream encrypted cine loops (short ultrasound video clips) for over-read within seconds—no onsite cardiologist or PACS (picture archiving and communication system) required. This model embodies the three pillars of AI-powered ultrasound: guided image acquisition, workflow productivity, and clinical decision support. These aren’t buzzwords; they’re structural innovations—foundational pieces for a smarter, faster, more equitable system of care.
Together they’re not just delivering sharp images or fast scans; they’re helping reimagine access to care itself.
Here’s how each pillar functions in the real world—and why together they’re transforming access to diagnostic services.
Guided Ultrasound: Turning complexity into confidence
If you’ve ever watched an ultrasound exam, you know it’s part science and part art. A trained sonographer knows where to place the probe, senses exactly how to angle it to find the right “window,” and capture an image that tells a clinical story. However, there’s a disconnect: according to the NIH, there was a significant difference between supply and demand of sonographers with the number of sonography graduates (2011-2021) increasing from 4,386 to 5,393 (+23.0%) while the number of open sonographer positions (2012-2021) increased from 18,462 to 25,162 (+36.3%).2
AI-driven devices such as the GE HealthCare VScan Air handheld scanner, powered by Caption Guidance, are helping close that gap. Features that enable accessibility include turn-by-turn on-screen instructions, a colored quality meter that helps visualize the image quality, and Auto Capture that freezes and stores the best clip, the moment quality thresholds are met. These features allow clinicians with minimal training to conduct scans accurately at the point of care.
Workflow productivity: Turning minutes into care
Every hospital I visit tells the same story: “We’re short-staffed, burned out, and there aren’t enough hours in the day.” AI can’t clone clinicians, but it can hand them back precious minutes. Embedded in the ultrasound workflow, AI automates keystrokes, aligns views, and follows preset scanning “recipes.” . A GE HealthCare study showed a 65 percent gain in efficiency and up to an 81 percent reduction in scan time: which is the difference between treating ten patients or fifteen in a shift.3
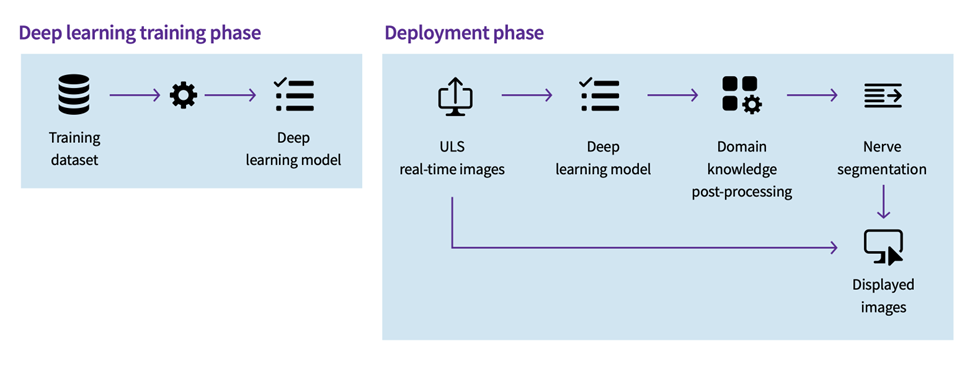
Across specialty consoles, intelligent automated protocols deliver further gains. For example, an internal study showed that cNerve shortens peripheral-nerve scouting by 81% while eliminating 93% of keystrokes. Integrated obstetric software automatically detects all 21 recommended fetal views and trims second-trimester cerebral biometry time by 65%. Meanwhile, shock evaluation and auto-Doppler tools center views on key organs, resize the blood flow box by about 20 percent faster, and vascular assistants cut keystrokes by 50 percent.4
Clinical decision support: Turning insight into action
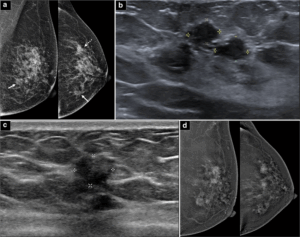
Reading images can be as time-consuming as acquiring them. AI add-ons can help complete checklists and help calculate risk in seconds. When evaluating a thyroid lump, for example, the Thyroid Assistant powered by Koios DS measures shape, edges, and brightness, then matches the findings to TIRADS—the Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System—to estimate cancer risk. A similar assistant for breast scans applies BIRADS criteria and has cut unnecessary biopsies by about two-thirds.5
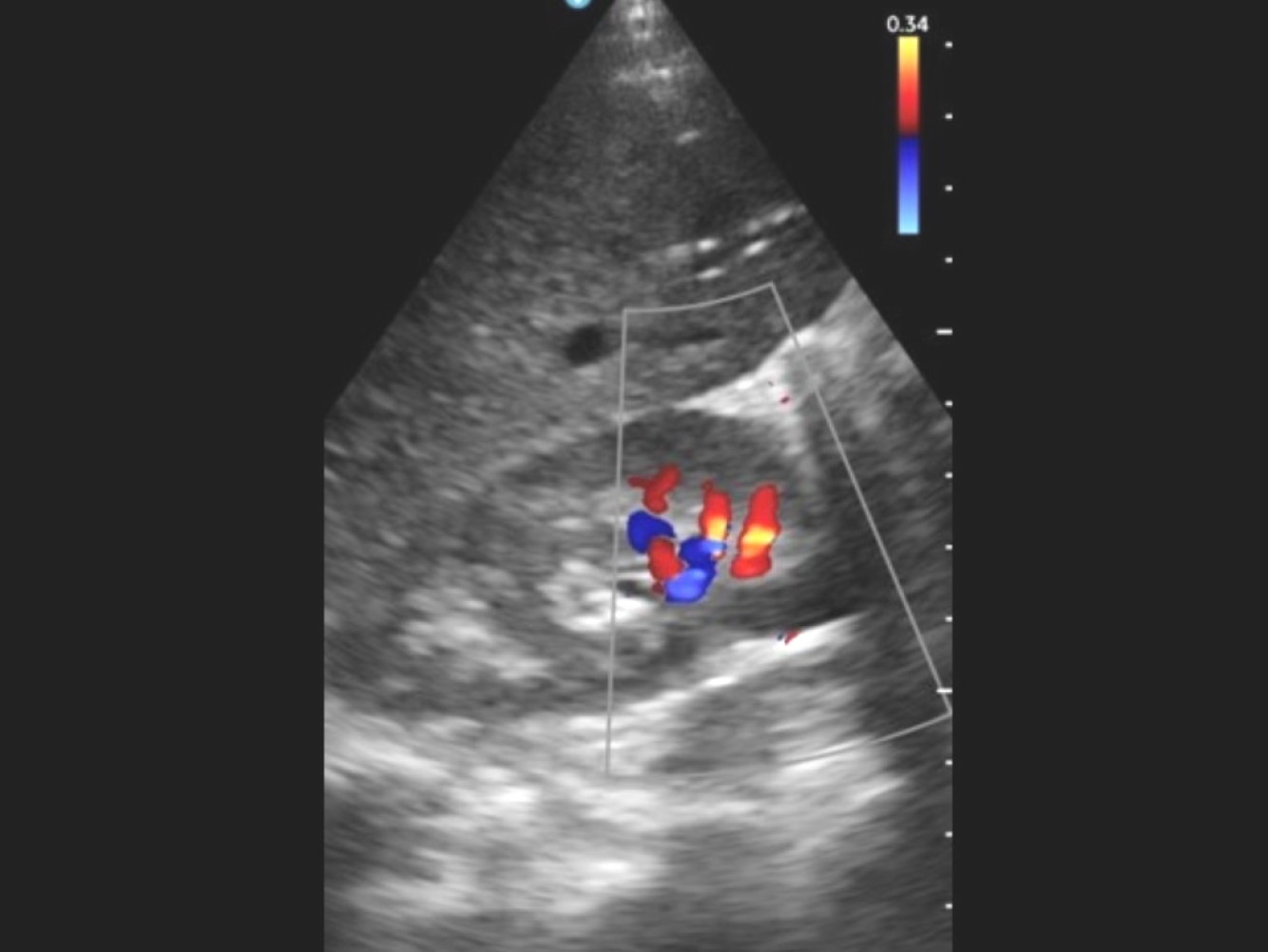
In addition, the Auto EF feature can calculate the left ventricular ejection fraction (the percentage of blood the heart pumps each beat) from three standard views—PLAX, AP2, and AP4—without manual tracing, cutting cardiac quantification to seconds.
Decision-support engines like Easy AFI deliver single-click global and segmental heart muscle strain in under ten seconds with no manual contouring required. The AI thyroid worksheet’s neural network assesses echogenicity, margins, and microcalcifications automatically. The breast imaging assistant fuses brightness-mode and tissue-stiffness data to output malignancy probability in two seconds6. In heart scans, an AI Doppler tool measures how fast blood moves through all four major valves and sums up the results with 98 percent accuracy.7 Across the board, these features bring specialist-grade insight to U.S. counties and areas across the world, where as many as 4.5 billion people lack access to quality care.
This is what keeps me going: envisioning a future where a woman in a rural town doesn’t drive hours for a pregnancy scan, where an overburdened ER nurse can rule out heart failure in minutes, and where a community health worker armed with a pocket-sized probe, AI guidance, and secure cloud collaboration can diagnose early, intervene quickly, and save lives. Guided ultrasound, workflow productivity, and clinical decision support are more than an imaging framework—they’re a blueprint for equitable care. With each breakthrough, diagnostic power moves closer to the patient, lowering barriers, and restoring dignity. And for people like Mark, this offers something even more valuable than technology: it offers peace of mind.
- https://www.cdc.gov/heart-disease/data-research/facts-stats/index.html ↩︎
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38534218/ ↩︎
- Venue Family R4 cNerve study DOC2725435 ↩︎
- JB20479XX / DOC 2727504 ↩︎
- Automated, low-cost palpable breast lump triage for countries”
Authors: Love SM, Berg WA, Podilchuk C, et al.
Presented at the 2016 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium ↩︎ - Cancer Res. 2017;77(4 Suppl):Abstract nr PD3-01 – Breast AI study presented at the 2016 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium ↩︎
- Source: GE internal data (DOC2292732 ↩︎